Metformin is a widely prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes. It helps control blood sugar levels effectively. However, recent discussions highlight a key concern: the relationship between Metformin and Vitamin B12. Long-term use of Metformin may lead to Vitamin B12 deficiency. This deficiency can result in serious health issues, such as anemia and nerve damage.
Many patients taking Metformin may not be aware of this connection. Reports suggest that nearly 30% of users experience reduced Vitamin B12 levels. Regular testing is essential for these individuals. Lack of awareness could lead to overlooked symptoms or unnecessary complications.
Understanding the link between Metformin and Vitamin B12 is vital. It can help patients manage their health better. They should stay informed and consult healthcare professionals about monitoring Vitamin B12 levels. Neglecting this relationship could mean living with potential health risks.
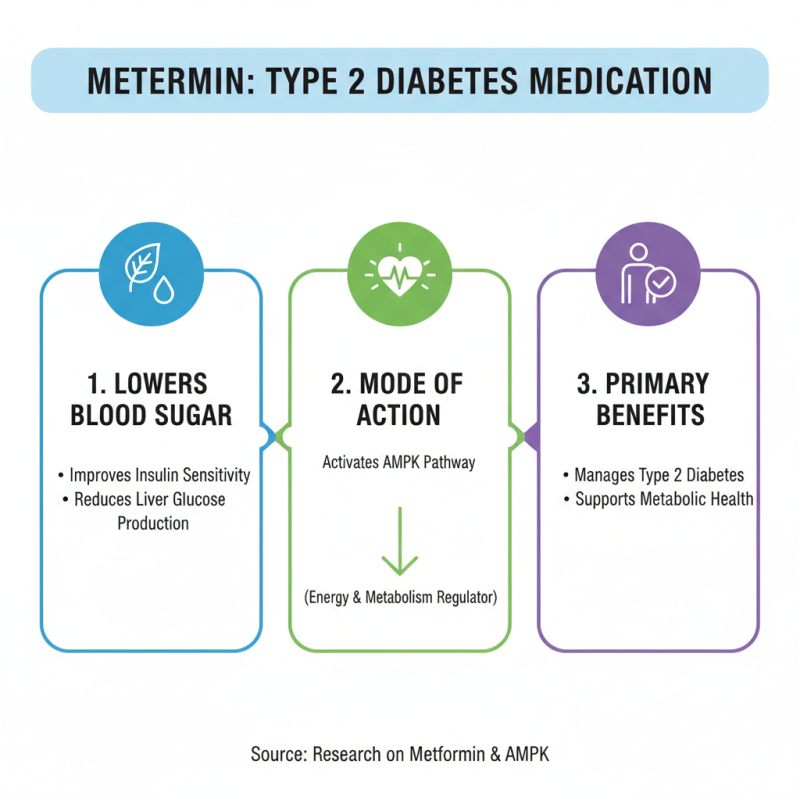
Metformin is a widely prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes. It helps lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity. Research shows that metformin can reduce glucose production in the liver. The drug primarily achieves its effects through the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. This pathway plays a crucial role in energy balance and metabolism.
In a study published in Diabetes Care, metformin was shown to reduce HbA1c levels by an average of 1.5 to 2 percentage points in patients. This is significant for managing diabetes effectively. However, one aspect that needs attention is the potential vitamin B12 deficiency associated with long-term use of metformin. Data suggests that up to 30% of patients on metformin may experience lower levels of vitamin B12 over time. This deficiency can lead to various health issues, including neuropathy and anemia.
Patients should monitor their vitamin B12 levels regularly. Sometimes the effects of metformin are not fully understood. More research is needed to explore the long-term implications of using this medication alongside possible nutritional deficiencies. Effective management of diabetes should consider both blood sugar control and overall nutrient status. This holistic approach may improve patient outcomes significantly.
Vitamin B12 plays a critical role in the body. It helps produce red blood cells and DNA. This vitamin is essential for nerve health. Without enough B12, one may experience fatigue, weakness, and even neurological issues. Many people overlook its importance. Food sources include meat, dairy, and eggs. For those on a vegan diet, fortified foods or supplements are necessary.
The symptoms of B12 deficiency can be subtle and easily ignored. Some might feel tired but attribute it to a busy lifestyle. Cognitive functions can also decline. Memory issues could stem from low B12 levels. Regular testing is advisable, especially for at-risk populations. Awareness can lead to better health choices. Ultimately, maintaining adequate B12 levels can enhance overall well-being. It’s not always straightforward. Some people may have absorption issues even with adequate intake. This complicates the relationship with B12 and health.
This chart illustrates the relationship between Metformin usage and Vitamin B12 levels over five years. The data suggests a correlation between Metformin treatment and a decrease in Vitamin B12 levels, emphasizing the importance of monitoring B12 status in patients using Metformin.
Metformin is a widely-used medication for managing type 2 diabetes. While it effectively lowers blood sugar levels, it can also have an impact on vitamin B12 levels. Studies indicate that long-term use of metformin may lead to a decrease in B12 absorption, leading to potential deficiencies. This issue is particularly important for patients on metformin for extended periods.
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in maintaining energy levels and ensuring proper nerve function. Symptoms of deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, and even neurological issues. It's interesting to note that not every person taking metformin experiences a decrease in B12, but the risk exists. Regular monitoring might be necessary for those on prolonged treatment.
There are some debates around this topic. Not all healthcare providers agree on the necessity of B12 supplementation for metformin users. Individual responses to the drug can vary significantly. Some people remain unaware of the potential impacts. This discrepancy can leave patients vulnerable to deficiencies without knowing it. Understanding this relationship becomes essential for those taking metformin to prioritize their overall health.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to several concerning symptoms. Many individuals may not realize they are deficient until serious issues arise. Common signs include fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. Some may experience dizziness or shortness of breath, especially during physical activities. Memory problems and mood changes can also occur, leading to confusion and irritability.
Over time, a lack of B12 can result in nerve damage. This may manifest as tingling sensations or numbness in the hands and feet. Confusion or difficulty concentrating can also develop. Cognitive decline in severe cases can significantly impact daily life. Many who rely on medications like metformin should monitor their B12 levels closely.
Regular blood tests can help detect deficiencies early on. Symptoms might be subtle, making them easy to overlook. Awareness is crucial, as untreated deficiencies can lead to long-term complications. Exploring dietary options to boost B12 intake is also essential. Reflecting on one's health and symptoms may help highlight this important nutrient's value.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Metformin Usage | Commonly prescribed for Type 2 diabetes management. |
| Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms | Fatigue, weakness, constipation, loss of appetite, numbness. |
| Common Risks of Deficiency | Anemia, nerve damage, cognitive difficulties. |
| Importance of Monitoring B12 | Regular testing recommended for long-term metformin users. |
| Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) | 2.4 mcg per day for adults. |
| Food Sources of Vitamin B12 | Meat, fish, dairy products, fortified cereals. |
| Potential Treatment for Deficiency | Oral supplements or intramuscular injections depending on severity. |
Metformin is widely used for managing diabetes.
However, its relationship with vitamin B12 is critical.
Long-term use of metformin can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency. This deficiency can result in various health issues, including anemia and neuropathy.
Monitoring B12 levels regularly is essential for those on metformin.
Healthcare providers often recommend testing vitamin B12 levels at least once a year for individuals taking metformin.
If levels are low, supplementation may be necessary. Vitamin B12 supplementation can be administered orally or through injections.
It's crucial to discuss options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach.
Dietary sources of vitamin B12 include meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
However, not everyone can obtain adequate B12 from diet alone. Real-life experiences show that some patients forget to follow through with monitoring, leading to deficiencies.
Individuals must remain proactive about their health. Awareness of potential issues can help address deficiencies before they worsen.