Folic Acid, a crucial B-vitamin, plays an essential role in maintaining overall health and well-being, particularly in the prevention of neural tube defects during pregnancy. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in nutritional science, "Folic Acid is not just a vitamin; it is a vital component in the intricate process of cellular repair and growth." This underscores the importance of understanding its benefits and sources, as well as addressing common misconceptions surrounding this key nutrient.
Incorporating adequate Folic Acid into one’s diet can lead to numerous health advantages, including improved cardiovascular health, brain function, and even mood enhancement. It is found abundantly in leafy greens, legumes, and fortified foods, making it accessible for many. However, despite its availability, many individuals still fall short of the recommended daily intake, emphasizing the need for increased awareness and education about its significance.
As we explore the various facets of Folic Acid—its benefits, dietary sources, and frequently asked questions—this knowledge can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that support their health and well-being. Understanding Folic Acid is more than just a matter of nutrition; it is a step towards fostering a healthier future for ourselves and our families.

Folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, plays a crucial role in the synthesis of DNA and the production of red blood cells. This essential nutrient is particularly important for women during pregnancy, as it helps in the proper development of the fetus and can significantly reduce the risk of neural tube defects. Additionally, folic acid supports brain health and can aid in mood regulation, making it vital for overall well-being.
Tip: To ensure you’re getting enough folic acid, incorporate a variety of leafy greens, legumes, and fortified grains into your diet. Foods like spinach, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources that can easily enhance your meals.
Understanding the importance of folic acid goes beyond just prenatal health. It is fundamental for everyone, promoting cardiovascular health and potentially lowering the risk of certain types of cancer. Regularly consuming adequate amounts of folic acid can help maintain proper cell function and contribute to a robust immune system.
Tip: If you struggle to meet your folic acid needs through diet alone, consider speaking with a healthcare professional about the possibility of taking a supplement to fill in any gaps.
Folic acid, a B-vitamin, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. One of its primary benefits is its ability to support cellular function and tissue growth. This is especially vital during periods of rapid development, such as during pregnancy, as folic acid helps prevent neural tube defects in the developing fetus. The nutrient aids in the production of DNA and RNA, making it essential for cell division and growth, which impacts various bodily functions.
Moreover, folic acid contributes to cardiovascular health by helping to lower homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to heart disease when present in high amounts. Regular intake of folic acid has also been associated with improved mental health, potentially reducing risks of depression and cognitive decline. Ensuring adequate folic acid levels through a balanced diet or supplements can thus greatly influence overall wellness, making it a vital nutrient for individuals at all life stages.
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Folic acid is a B-vitamin (B9) essential for cell growth and metabolism. |
| Benefits | Supports DNA synthesis, reduces risk of neural tube defects during pregnancy, and may improve heart health. |
| Sources | Dark leafy greens, legumes, nuts, seeds, and fortified cereals. |
| Recommended Daily Intake | 400 micrograms for adults; 600 micrograms for pregnant women. |
| Deficiency Symptoms | Fatigue, weakness, irritability, and megaloblastic anemia. |
| FAQs | What is the best time to take folic acid? It is best taken daily, especially before and during pregnancy. |
Folic acid, a vital B-vitamin (B9), plays a significant role in DNA synthesis and repair, making it essential for proper cell growth and function. For those looking to increase their intake of this nutrient naturally, incorporating specific foods into your diet can be quite beneficial.
 Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and romaine lettuce are excellent sources of folic acid. Additionally, legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are packed with this nutrient and can easily be added to salads, soups, or stews.
Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and romaine lettuce are excellent sources of folic acid. Additionally, legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are packed with this nutrient and can easily be added to salads, soups, or stews.
Incorporating a variety of foods rich in folic acid into your meals can enhance your overall health. Fruits such as oranges, bananas, and avocados are not only delicious but also contribute significantly to your daily folic acid intake. Whole grains, including quinoa and brown rice, offer an additional boost.
Tips: To maximize your folic acid intake, consider preparing dishes that include multiple sources of this nutrient, like a quinoa salad with black beans, spinach, and diced oranges. Also, cooking methods matter; steaming vegetables rather than boiling helps retain more folic acid, allowing you to enjoy its full benefits! Embracing these food sources can help you maintain optimal health and well-being.
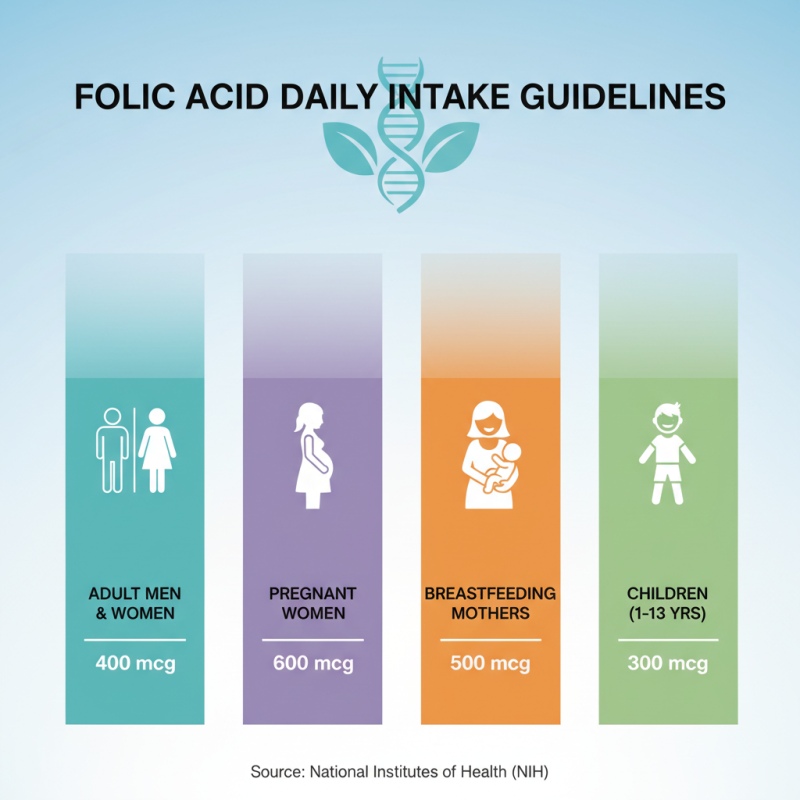
The recommended daily intake of folic acid varies according to age, gender, and specific life circumstances. According to the National Institutes of Health, adult men and women should aim for 400 micrograms (mcg) per day, while pregnant women require significantly more—about 600 mcg—to support fetal development and prevent neural tube defects. Breastfeeding mothers are advised to take 500 mcg daily to ensure adequate nutrient supply for both the mother and infant.
Certain populations may have increased needs for folic acid. For instance, women planning to conceive are encouraged to begin folic acid supplementation at least one month prior to conception, aligning with research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which highlights that adequate folate levels can reduce the risk of birth defects by up to 70%. Additionally, people with certain medical conditions, such as malabsorption syndromes or chronic alcoholism, may require higher doses, as these factors can impair folate uptake. Understanding these guidelines is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing deficiencies in diverse groups.
Folic acid, also known as vitamin B9, plays a crucial role in DNA synthesis and repair, making it particularly important during periods of rapid growth such as pregnancy and infancy. Many individuals have questions about its benefits and sources. Among the most common queries is how much folic acid one should consume daily. For adults, the recommended dietary allowance is typically around 400 micrograms, but this increases to 600 micrograms for pregnant women to support fetal development and prevent neural tube defects.
Another frequent question pertains to dietary sources of folic acid. Leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and fortified foods are excellent sources of this vital nutrient. Additionally, some people wonder if supplementation is necessary. While a balanced diet can provide adequate amounts, certain individuals—such as those with specific health conditions or dietary restrictions—may require additional folic acid supplements to meet their needs. Understanding these aspects helps individuals make informed decisions regarding their nutrition and health.
This bar chart presents the daily recommended intake of Folic Acid in micrograms (mcg) for different age groups, highlighting the importance of appropriate levels for overall health.






